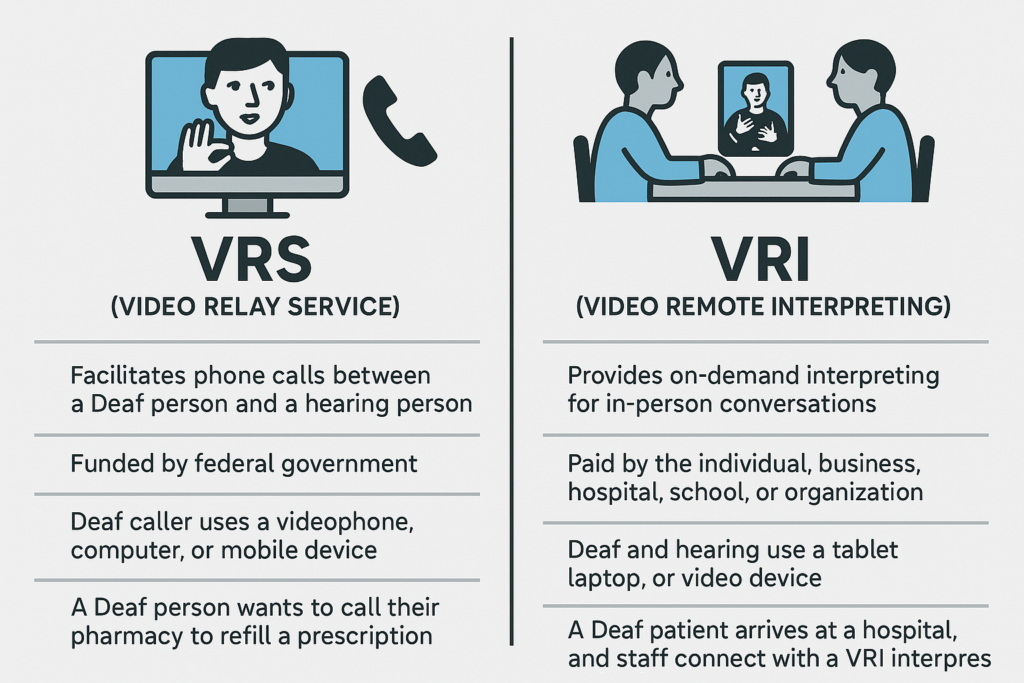
| Purpose | Facilitates phone calls between a Deaf person and a hearing person using a sign language interpreter. | Provides on-demand interpreting for in-person conversations when a Deaf and hearing person are physically together but need an interpreter remotely. |
| Who Pays | Funded by the federal government (FCC) — it’s free to users. | Paid by the individual, business, hospital, school, or organization requesting the service. |
| Situation Used | Deaf person needs to call a business, friend, doctor, etc., or a hearing person needs to call a Deaf person. | A Deaf person and a hearing person are in the same room (like at a hospital, office, police station) but no in-person interpreter is available. |
| Setup | Deaf caller uses a videophone, computer, or mobile device to connect to a VRS interpreter who then makes a phone call to the hearing party. | Deaf and hearing individuals use a tablet, laptop, or video device placed in the room to connect to a remote interpreter. |
| Example | A Deaf person wants to call their pharmacy to refill a prescription. | A Deaf patient arrives at a hospital emergency room, and staff connect with a VRI interpreter on an iPad to assist with communication. |
| Regulations | Highly regulated by the FCC (Federal Communications Commission). | Less regulation — follows general ADA (Americans with Disabilities Act) guidelines but not managed by the FCC. |